前言
WordPress 是一款免费且开源的内容管理系统 (CMS)。由于其插件架构和模板系统的高度可扩展性,大部分管理工作都可以通过 Web 界面完成。正因如此,WordPress 成为创建各种类型网站(从博客到产品页面再到电子商务网站)的热门选择。
通常情况下,运行 WordPress 需要安装 LAMP(Linux、Apache、MySQL 和 PHP)或 LEMP(Linux、Nginx、MySQL 和 PHP)堆栈,这可能会非常耗时。然而,通过使用 Docker 和 Docker Compose 等工具,您可以简化设置过程。无需手动安装每个组件,只需使用标准化的镜像,这些镜像包含库、配置文件和环境变量等内容。然后,您可以在共享操作系统上运行这些独立的容器。
在本教程中,您将构建一个多容器的 WordPress 安装环境。您的容器将包括一个 MySQL 数据库、一个 Nginx Web 服务器和 WordPress 本身。为了保护您的安装,您还将使用 Let’s Encrypt 获取与您的域名关联的 TLS/SSL 证书。最后,您将设置一个 cron 作业来更新您的证书,确保您的域名保持安全。
步骤
- 定义 Web 服务器配置
- 定义环境变量
- 在 Docker Compose 中定义服务
- 获取 SSL 证书
- 修改 Web 服务器配置
- 通过 Web 界面完成安装
- 启用 SSL 自动续订
一、定义web程序配置
1.创建项目目录
首先,创建一个项目目录。在此示例中,我将其命名为 wordpress。您可以根据需要选择不同的名称。
mkdir wordpress
2.创建配置目录和文件
进入 wordpress 目录,再创建一个 nginx-conf 目录,并在其中添加一个 nginx.conf文件进行网站配置。稍后我们会在 webserver 配置中用到它。
cd wordpress
mkdir nginx-conf
touch nginx-conf/nginx.conf
3.添加服务器配置
在 nginx.conf 文件中,添加一个服务器块,包含服务器名称、文档根目录的指令以及位置块。有关配置细节可以参考快速配置nginx的几种方法。这里我们暂时将 server_name 定义为 localhost,待本地运行测试正常后,再上传到服务器时修改为实际域名。
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name localhost;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
root /var/www/html;
location ~ /.well-known/acme-challenge {
allow all;
root /var/www/html;
}
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$is_args$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass wordpress:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off; access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
log_not_found off; access_log off; allow all;
}
location ~* \.(css|gif|ico|jpeg|jpg|js|png)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
}
编辑完成后保存并关闭文件。
二、定义环境变量
您的数据库和 WordPress 应用程序容器需要在运行时访问某些环境变量,以便保留并访问应用程序数据。这些变量包括敏感信息和非敏感信息。一般来说,不要在 Docker Compose 文件中设置所有这些值,而应在 .env 文件中设置敏感值并限制其流通,以防止这些值被复制到项目存储库并公开暴露。(在更严格的项目中,您可能需要通过服务器主机提供的密钥服务如亚马逊AWS Key来严格地管理这些值。) 在您的主项目目录中,打开一个名为 .env 的文件:
vi .env
您在此文件中设置的机密值包括 MySQL根用户的密码以及 WordPress 将用于访问数据库的用户名和密码。 将以下变量名称和值添加到文件中。请记住在此处为每个变量提供自己的值
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=your_root_password
MYSQL_USER=your_wordpress_database_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD=your_wordpress_database_password
编辑完成后保存并关闭文件。 由于 .env 文件包含敏感信息,您需要确保它包含在您的项目 .gitignore 和 .dockerignore 文件中。这将分别告诉 Git 和 Docker 哪些文件不应复制到您的 Git 存储库和 Docker 镜像中。
git init
然后创建并打开一个.gitignore文件:
vi .gitignore
添加到 .env 文件
.env
将其添加到 .dockerignore 文件中也是一个很好的预防措施,这样当您使用此目录作为构建上下文时,它就不会出现在您的容器中。
vi .dockerignore
添加.env到文件:
.env
在此之下,您可以选择添加与应用程序开发相关的文件和目录:
.env
.git
docker-compose.yml
.dockerignore
有了这些设置后,您现在可以继续在 docker-compose.yml 文件中定义您的服务。
三、使用 Docker Compose 定义服务
使用 docker compose,您可以定义不同的服务来运行多容器应用程序,因为 Compose 允许您将这些服务与共享网络和卷链接在一起。这将对您当前的设置很有帮助,因为您将为数据库、WordPress 应用程序和 Web 服务器创建不同的容器。您还将创建一个容器来运行Certbot 客户端以获取 Web 服务器的证书.
首先,创建并打开文件docker-compose.yaml:
vi docker-compose.yml
1.定义db服务
添加以下代码来定义您的 Compose 文件版本和db数据库服务:
# 在最新的文档中 version 已经过时,所以你可以不添加这个版本顶级元素
# version: '3.9'
services:
db:
image: mysql:8.0
container_name: db
restart: unless-stopped
env_file: .env
environment:
- MYSQL_DATABASE=wordpress
volumes:
- dbdata:/var/lib/mysql
# 修改数据库安全插件 不需要
# command: '--default-authentication-plugin=mysql_native_password'
networks:
- app-network
服务db定义包含以下选项:
- image:这告诉 Compose 要拉取哪个镜像来创建容器。您在此处固定镜像mysql:8.0以避免在mysql:latest继续更新镜像时发生冲突。
- container_name:指定容器的名称。
- restart:定义容器重启策略。默认为no,我们将容器设置为除非手动停止,否则将重新启动。
- env_file:此选项告诉 Compose 从 .env 文件添加环境变量。
- environment:允许您添加 .env 文件中定义的环境变量以外的其他环境变量。这里设置 MYSQL_DATABASE 变量为 wordpress。
- volumes:在这里,您将挂载一个名为 dbdata 的卷,该卷位于容器 /var/lib/mysql 目录中。这是大多数发行版中 MySQL 的标准数据目录。
- networks:这指定您的应用服务将加入 app-network 网络。
接下来,在 db 服务定义下方,添加您的 WordPress 应用程序服务的定义
2.定义wordpress
wordpress:
depends_on:
- db
image: wordpress:6.5.4-php8.1-fpm-alpine
container_name: wordpress
restart: unless-stopped
env_file: .env
environment:
- WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=db:3306
- WORDPRESS_DB_USER=$MYSQL_USER
- WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=$MYSQL_PASSWORD
- WORDPRESS_DB_NAME=wordpress
volumes:
- wordpress:/var/www/html
networks:
- app-network
在此服务定义中,您将命名容器并定义重启策略,就像对 db 服务所做的那样。您还将添加一些特定于此容器的选项:
-
depends_on:确保容器按依赖顺序启动,wordpress 容器在 db 容器之后启动。
-
image:这里我们使用 wordpress:6.5.4-php8.1-fpm-alpine 镜像。。如步骤 1中所述,使用此映像可确保您的应用程序具有php-fpm处理 PHP 所需的处理器。这也是一个alpine源自Alpine Linux 项目的映像,它将有助于降低您的整体映像大小。有关使用映像的优缺点以及这对您的应用程序是否有意义的详细信息,请查看Docker Hub WordPress 映像页面的“映像变体”alpine部分下的完整讨论。
-
env_file:指定从 .env 文件中提取值。
-
environment:使用 .env 文件中定义的值,但将它们分配给 WordPress 镜像所需的变量名。
-
volumes:将一个名为 wordpress 的卷挂载到 WordPress 镜像创建的 /var/www/html 挂载点。
-
networks:将 wordpress 容器添加到 app-network 网络。
接下来,在应用程序服务定义下方,为您的 Nginx 服务添加以下定义:
3.定义nginx服务
webserver:
depends_on:
- wordpress
image: nginx:nginx:1.27.0-alpine
container_name: webserver
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "8080:80"
volumes:
- wordpress:/var/www/html
- ./nginx-conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d
networks:
- app-network
在这里,您要命名容器并使其wordpress按启动顺序依赖于容器。您还将使用一个alpine图像 — nginx:1.27.0-alpine nginx 图像。
此服务定义还包括以下选项:
- ports:公开端口 80 以启用 nginx.conf 中定义的配置选项。
- volumes:在这里,您定义命名卷和绑定挂载的组合:
- wordpress:/var/www/html:这会将您的 WordPress 应用程序代码挂载到目录中,即您在 Nginx 服务器块中/var/www/html设置的目录。
- ./nginx-conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d:这会将主机上的 Nginx 配置目录绑定挂载到容器上的相关目录,确保您对主机上的文件所做的任何更改都将反映在容器中。
在webserver服务下方,添加您的网络和卷定义:
volumes:
wordpress:
dbdata:
networks:
app-network:
driver: bridge
在这个 Docker Compose 定义中,您定义了两个顶级的 volumes 键:wordpress 和 dbdata。当 Docker 创建这些卷时,它们的内容将存储在主机文件系统的 /var/lib/docker/volumes/ 目录下由 Docker 管理的目录中。然后,每个卷的内容都会从这个目录挂载到使用该卷的任何容器中。这样可以在容器之间共享代码和数据。 此外,您还定义了一个用户自定义的桥接网络 app-network。这个网络可以支持容器之间的通信,因为它们都位于同一个 Docker 守护进程主机上。这简化了应用程序内部的流量和通信,因为它在同一个桥接网络上打开了所有容器之间的端口,而不需要向外界公开任何端口。因此,您的 db、wordpress 和 webserver 容器可以相互通信,您只需要公开端口 80 以供前端访问应用程序即可
certbot 部分因为需要使用实际域名,我们先不定义,我们先在本地来测试容器是否能正常运行。
四、本地运行docker compose
使用docker-compose up命令启动容器,该命令将按照您指定的顺序创建并运行容器。通过添加标志-d,该命令将在后台运行db、wordpress和容器:webserver
docker-compose up -d
以下输出确认您的服务已创建:
[+] Running 3/6
⠇ Network wordpress-compose_app-network Created 0.8s
⠇ Volume "wordpress-compose_dbdata" Created 0.7s
⠇ Volume "wordpress-compose_wordpress" Created 0.7s
✔ Container db Started 0.3s
✔ Container wordpress Started 0.4s
✔ Container webserver Started 0.6s
使用docker-compose ps检查您的服务状态:
docker-compose ps
一旦完成,您的db、wordpress和webserver服务将会启动Up.
NAME IMAGE COMMAND SERVICE CREATED STATUS PORTS
db mysql:8.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" db 6 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 3306/tcp, 33060/tcp
webserver nginx:1.27.0-alpine "/docker-entrypoint.…" webserver 6 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 0.0.0.0:8080->80/tcp
wordpress wordpress:6.5.4-php8.1-fpm-alpine "docker-entrypoint.s…" wordpress 6 seconds ago Up 5 seconds 9000/tcp
现在访问你本地的地址http://localhost:8080/,你应该能看到下面的页面,你可以进行下一步进行安装。
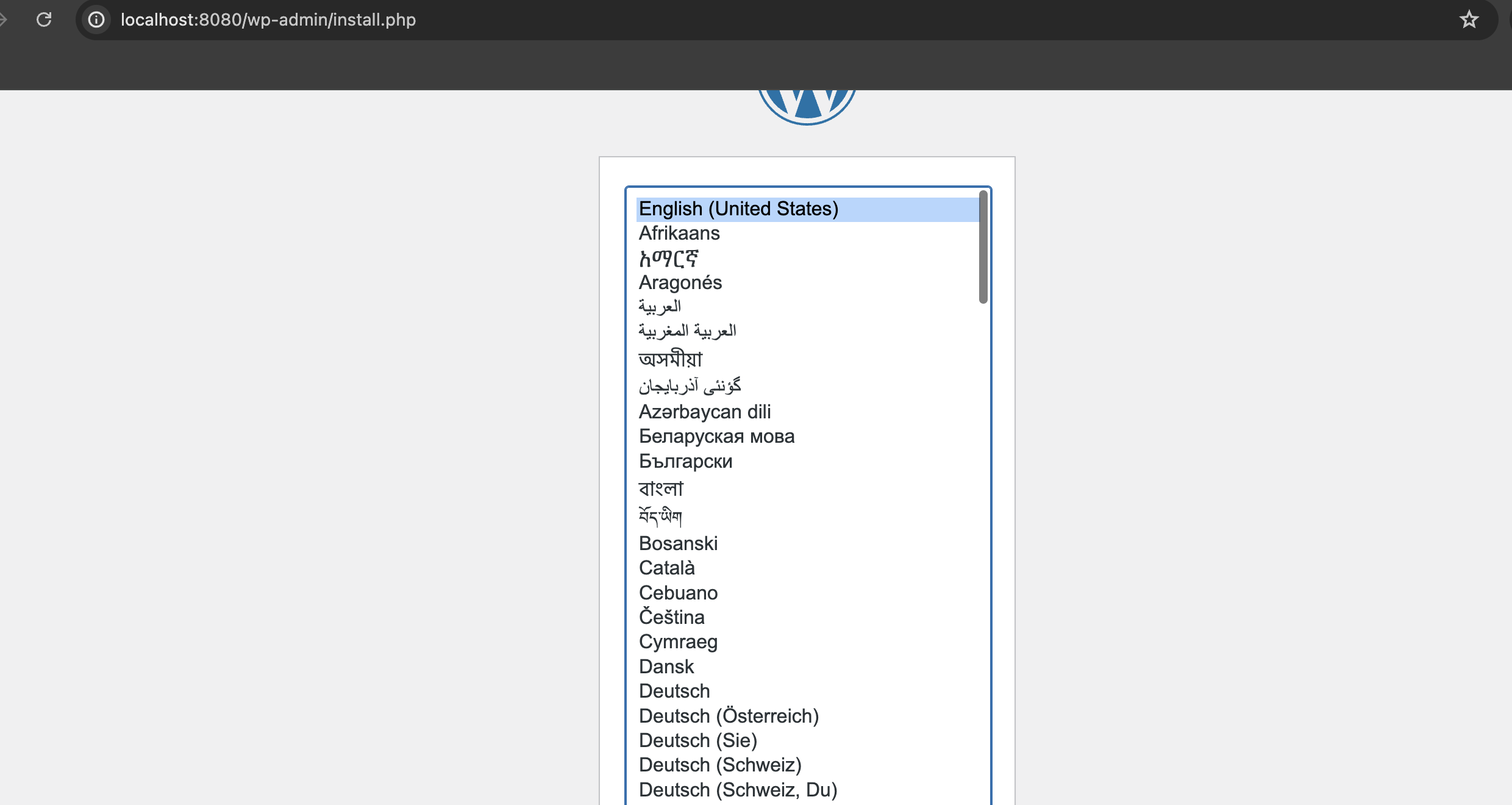
五、上传到 github 仓库
现在我们要把本地文件上传到服务器,你可以通过scp命令 复制到你的服务器,但是因为我们还要经过多次修改,所以我们最好是使用git来管理。
1.创建一个github仓库
登陆你的github账户,创建一个新的仓库。登陆你的账户点击
2.上传到github仓库
把本地修改上传到你的github仓库。
git init
git add .
git commit -m "init commit"
git remote set origin "你github项目地址"
git push origin main
七、在服务器上clone仓库
现在ssh 登陆你的服务器,一般来说服务器上其他的目录可能没有写入权限,所以最好是现到/tmp 目录,然后
git clone [email protected]:longlikun/docker-compose-wordpress.git
八、修改配置
我们创建一个新的分支来管理服务器上的内容修改
git checkout branh -b server <commit-hash>
1.修改env环境变量
把env.example 修改为 .env
mv env.example .env
这里的修改不多,我们就直接在服务器上使用vim来修改 然后添加里面的内容
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=blog.eimoon.com
MYSQL_USER=blog.eimoon.com
MYSQL_PASSWORD=blog_eimoon_com_password
2.修改端口
到nginx-conf/nginx.conf 文件中,把webserve的端口修改为"80:80" 这里要注意一下,如果你的服务器上已经运行了nginx或者其他运行在80端口的程序,要停止一下。 通过
sudo systemctl stop nginx
停止nginx。 然后查看运行在80端口的程序
ss -tulnp | grep 80
没有输出才正确,如果有输出,查看你的程序,如果能停止就停止一下。如果不能停止考虑使用反向代理来处理我们docker compose wordpress。
sudo kill -9 PID
3.修改域名
修改nginx 的配置,使用真实域名
server_name "你的已解析真实域名";
现在你可以到你的docker compose 文件目录运行 docker compose up -d 创建项目了。
稍等你一会,你就可以访问wordpress的安装页面了。
4. 把服务器修改推到github
git add
git commit -m "change webserv port and domain"
git push origin feat/new_port
五、本地添加certbot服务
1.本地修改docker compose 服务
因为修改的地方比较多,我们在本地修改。首先从服务器上拉取你的分支feat/new_port,然后在这分支修改,在您的webserver定义下方,最后一个服务定义certbot。请务必将此处列出的电子邮件地址和域名替换为您自己的信息:
certbot:
depends_on:
- webserver
image: certbot/certbot
container_name: certbot
volumes:
- certbot-etc:/etc/letsencrypt
- wordpress:/var/www/html
command: certonly --webroot --webroot-path=/var/www/html --email longlikun@your_domain --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staging -d your_domain -d www.your_domain
- 在这个定义还添加了一个command选项,用于指定与容器的默认certbot命令一起运行的子命令。该certonly子命令将使用以下选项获取证书:
- –webroot:这告诉 Certbot 使用 webroot 插件将文件放在 webroot 文件夹中进行身份验证。此插件依赖于HTTP-01 验证方法,该方法使用 HTTP 请求来证明 Certbot 可以从响应给定域名的服务器访问资源。
- –webroot-path:指定 webroot 目录的路径。
- –email:您用于注册和恢复的首选电子邮件。
- –agree-tos:这表明您同意ACME 的订户协议。
- –no-eff-email:这告诉 Certbot 您不希望与电子前沿基金会(EFF) 共享您的电子邮件。如果您愿意,可以省略此项。
- –staging:这告诉 Certbot 您希望使用 Let’s Encrypt 的暂存环境来获取测试证书。
- -d:这允许您指定要应用于请求的域名。在本例中,您已包括your_domain和。请务必将它们替换为您自己的域名。www.your_domain
同时我们还要在主volume中添加
certbot-etc
volumes:
certbot-etc: # 添加这一行
wordpress:
dbdata:
以下是docker-compose.yml完整文件:
services:
db:
container_name: db
image: mysql:8.0
env_file: .env
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- MYSQL_DATABASE=wordpress
volumes:
- dbdata:/var/lib/mysql
networks:
- app-network
wordpress:
depends_on:
- db
container_name: wordpress
image: wordpress:6.5.4-php8.1-fpm-alpine
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
WORDPRESS_DB_HOST: db:3306
WORDPRESS_DB_USER: $MYSQL_USER
WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD: $MYSQL_PASSWORD
WORDPRESS_DB_NAME: wordpress
volumes:
- wordpress:/var/www/html
networks:
- app-network
webserver:
depends_on:
- wordpress
container_name: webserver
image: nginx:1.27.0-alpine
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- wordpress:/var/www/html
- ./nginx-conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d
networks:
- app-network
certbot:
depends_on:
- webserver
image: certbot/certbot
container_name: certbot
volumes:
- certbot-etc:/etc/letsencrypt
- wordpress:/var/www/html
command: certonly --webroot --webroot-path=/var/www/html --email longlikun@your_domain --agree-tos --no-eff-email --staging -d your_domain -d www.your_domain
volumes:
wordpress:
dbdata:
certbot-etc:
networks:
app-network:
driver: bridge
2.上传到github
把修改上传到github仓库
git add .
git commit -m "add certbot server"
git push origin feat/new_port
3.服务器拉取合并最新修改
git pull origin feat/new_port
git switch feat/new_port
4.服务器上运行最新的docker-compose
docker compose down -v
docker compose up -d
5. 查看测试证书
docker-compose exec webserver ls -la /etc/letsencrypt/live
正常是这样的输出
Output
total 16
drwx------ 3 root root 4096 May 10 15:45 .
drwxr-xr-x 9 root root 4096 May 10 15:45 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 740 May 10 15:45 README
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 10 15:45 your_domain
6. 获取真实证书
修改docker-compose文件,把–staging指令去掉,添加–force-renewal参数来获取真实证书。
command: certonly --webroot --webroot-path=/var/www/html --email [email protected] --agree-tos --no-eff-email --force-renewal -d www.your_domain
现在重新运行docker-compose 构建certbot
docker-compose up --force-recreate --no-deps certbot
–no-deps 告诉 Compose 它可以跳过启动 webserver 服务,因为它已经在运行了
看到类似的日志代表请求成功
Recreating certbot ... done
Attaching to certbot
certbot | Saving debug log to /var/log/letsencrypt/letsencrypt.log
certbot | Plugins selected: Authenticator webroot, Installer None
certbot | Renewing an existing certificate
certbot | Performing the following challenges:
certbot | http-01 challenge for your_domain
certbot | http-01 challenge for www.your_domain
certbot | Using the webroot path /var/www/html for all unmatched domains.
certbot | Waiting for verification...
certbot | Cleaning up challenges
certbot | IMPORTANT NOTES:
certbot | - Congratulations! Your certificate and chain have been saved at:
certbot | /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/fullchain.pem
certbot | Your key file has been saved at:
certbot | /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/privkey.pem
certbot | Your cert will expire on 2019-08-08. To obtain a new or tweaked
certbot | version of this certificate in the future, simply run certbot
certbot | again. To non-interactively renew *all* of your certificates, run
certbot | "certbot renew"
certbot | - Your account credentials have been saved in your Certbot
certbot | configuration directory at /etc/letsencrypt. You should make a
certbot | secure backup of this folder now. This configuration directory will
certbot | also contain certificates and private keys obtained by Certbot so
certbot | making regular backups of this folder is ideal.
certbot | - If you like Certbot, please consider supporting our work by:
certbot |
certbot | Donating to ISRG / Let's Encrypt: https://letsencrypt.org/donate
certbot | Donating to EFF: https://eff.org/donate-le
certbot |
certbot exited with code 0
十 nginx 安全证书配置
修改nginx 配置如下
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name your_domain www.your_domain;
location ~ /.well-known/acme-challenge {
allow all;
root /var/www/html;
}
location / {
rewrite ^ https://$host$request_uri? permanent;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name your_domain www.your_domain;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
root /var/www/html;
server_tokens off;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/privkey.pem;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/options-ssl-nginx.conf;
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src * data: 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline'" always;
# add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains; preload" always;
# enable strict transport security only if you understand the implications
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$is_args$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass wordpress:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off; access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
log_not_found off; access_log off; allow all;
}
location ~* \.(css|gif|ico|jpeg|jpg|js|png)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
}
options-ssl-nginx.conf 这个文件可以用通过这个命令获取
curl -sSLo nginx-conf/options-ssl-nginx.conf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/certbot/certbot/master/certbot-nginx/certbot_nginx/_internal/tls_configs/options-ssl-nginx.conf
在webserver中添加443端口
修改docker-compose 文件,在webserver中添加443端口
webserver:
depends_on:
- wordpress
image: nginx:1.27-alpine
container_name: webserver
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "80:80"
- "443:443"
volumes:
- wordpress:/var/www/html
- ./nginx-conf:/etc/nginx/conf.d
- certbot-etc:/etc/letsencrypt
networks:
- app-network
然后重新创建webserver
docker-compose up -d --force-recreate --no-deps webserver
检查状态
然后查看 docker compose ps
应该是类似的输出
Output
Name Command State Ports
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
certbot certbot certonly --webroot ... Exit 0
db docker-entrypoint.sh --def ... Up 3306/tcp, 33060/tcp
webserver nginx -g daemon off; Up 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:80->80/tcp
wordpress docker-entrypoint.sh php-fpm Up 9000/tcp
然后访问你的页面dockerwp.eimoon.com,应该是能通过https访问了。
十一 自动更新证书
Let’s Encrypt 证书的有效期为 90 天。你可以设置自动更新流程,确保证书不会失效。一种方法是使用 cron 计划工具创建一个作业。在下面的示例中,你将创建一个 cron 作业,定期运行一个脚本,更新证书并重新加载 Nginx 配置。
1.定义脚本文件
在你的项目目录下创建一个ssl_renew.sh脚本
#!/bin/bash
COMPOSE="/usr/local/bin/docker-compose --no-ansi"
DOCKER="/usr/bin/docker"
#修改为你项目目录
cd /home/wordpress/
$COMPOSE run certbot renew --dry-run && $COMPOSE kill -s SIGHUP webserver
这个脚本首先将 docker-compose 二进制文件赋值给一个名为 COMPOSE 的变量,并指定了 –no-ansi 选项,该选项将运行不带 ANSI 控制字符的 docker-compose 命令。然后,它对 docker 二进制文件做了同样的操作。最后,它会切换到 ~/wordpress 项目目录,并运行以下 docker-compose 命令:
docker-compose run:这将启动一个 certbot 容器,并覆盖 certbot 服务定义中提供的命令。不使用 certonly 子命令,而是使用 renew 子命令,它将更新即将过期的证书。此外,还包括用于测试脚本的 –dry-run 选项。 docker-compose kill:它会向 webserver 容器发送 SIGHUP 信号,以重新加载 Nginx 配置。
给这个文件添加执行权限
chmod +x ssl_renew.sh
测试脚本
接下来,打开根 crontab 文件,按指定时间间隔运行更新脚本:
sudo crontab -e
现设置为3分钟来测试一下
*/3 * * * * /home/sammy/wordpress/ssl_renew.sh >> /var/log/cron.log 2>&1
这将把任务间隔设置为每三分钟一次,以便您可以测试续订请求是否按计划进行。将创建一个日志文件 cron.log,以记录作业的相关输出
这样的输出代表更新正确
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates below have not been saved.)
Congratulations, all renewals succeeded. The following certs have been renewed:
/etc/letsencrypt/live/your_domain/fullchain.pem (success)
** DRY RUN: simulating 'certbot renew' close to cert expiry
** (The test certificates above have not been saved.)
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
修改实际实际
然后修改 crontab 文件,设置每天的运行间隔。例如,要在每天中午运行脚本,可以修改文件的最后一行,如下所示:
0 12 * * * /home/sammy/wordpress/ssl_renew.sh >> /var/log/cron.log 2>&1
还需要删除 ssl_renew.sh 脚本中的 –dry-run 选项,完整后最总的ssl_renew.sh文件如下:
#!/bin/bash
COMPOSE="/usr/local/bin/docker-compose --no-ansi"
DOCKER="/usr/bin/docker"
#修改为你实际的文件夹
cd /home/wordpress/
$COMPOSE run certbot renew && $COMPOSE kill -s SIGHUP webserver
您的 cron 作业会在 Let’s Encrypt 证书到期时对其进行更新,确保证书不会失效。
总结
在本教程中,您使用 Docker Compose 创建了一个带有 Nginx Web 服务器的 WordPress 安装。作为工作流程的一部分,您为希望与 WordPress 网站关联的域获取了 TLS/SSL 证书。此外,您还创建了一个 cron 作业,以便在必要时更新这些证书。
关注我获取更多资讯


